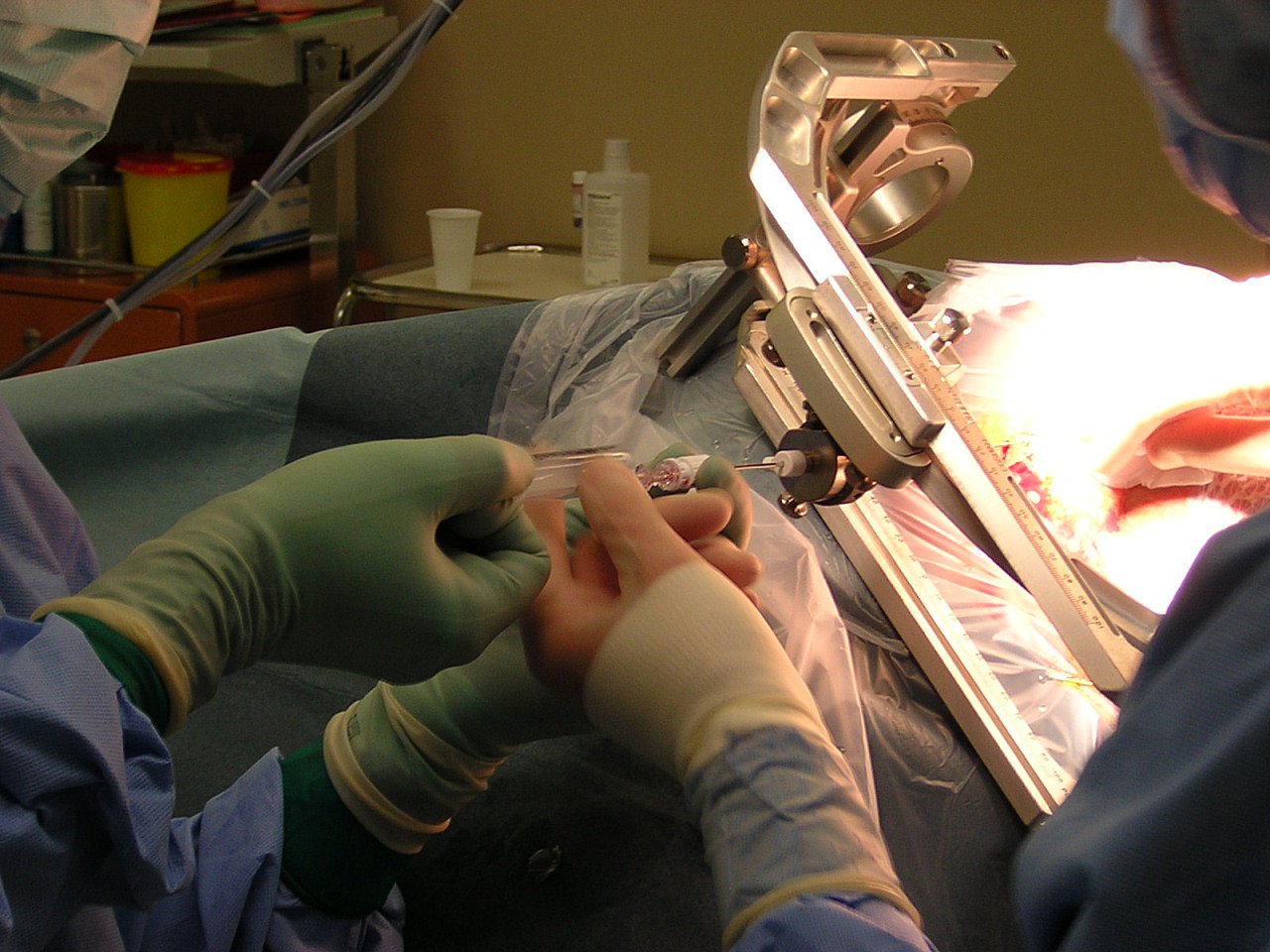
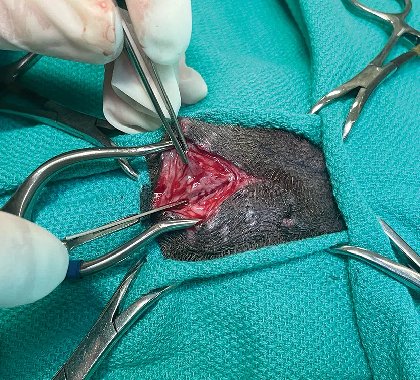
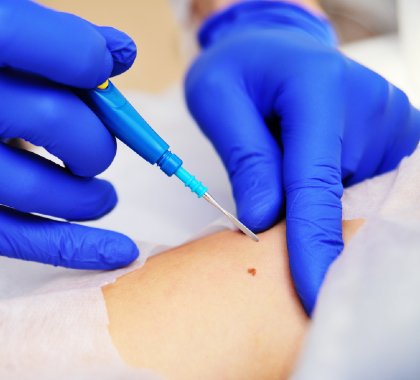
Biopsy is a medical procedure used to obtain tissue samples from the body for microscopic examination. These samples are collected to diagnose various medical conditions, including cancer, infections, inflammatory diseases, and autoimmune disorders. Biopsies can be performed on different parts of the body, such as the skin, breast, liver, lung, prostate, or gastrointestinal tract, depending on the suspected condition.
During a biopsy, a healthcare professional extracts a small piece of tissue using specialized instruments, such as a needle, forceps, or scalpel. The tissue sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis by a pathologist, who examines it under a microscope to identify any abnormal cells or tissue structures.
There are several types of biopsies, including needle biopsies (such as core needle biopsy or fine-needle aspiration biopsy), surgical biopsies, endoscopic biopsies, and skin biopsies. The choice of biopsy method depends on factors such as the location and size of the suspected abnormality, as well as the patient’s overall health and medical history.
Biopsy results play a crucial role in determining the appropriate course of treatment for patients. By providing detailed information about the nature and extent of a disease, biopsy findings help healthcare professionals develop personalized treatment plans tailored to each individual’s needs, ultimately contributing to improved health outcomes and quality of life.